What is Subnetting and Why is It Important?
Imagine you’re managing a network where thousands of devices are communicating. Subnetting is like dividing the network into smaller sections, or subnets, so that everything can be efficiently managed. Just as cities are divided into their regions and further into neighborhoods to make services like water, electricity, and garbage collection easier, subnetting helps you organize networks in a way which optimizes usage of IP address, increases its security, and ensures better performance of the network.
With the rapid growth of the internet, the number of connected devices is continuously rising. Without subnetting, networks could have serious problems like depletion of IP addresses, performance bottlenecks, and security risks. Subnetting is essential to solve these issues and ensure smooth communication between the devices.
How Subnetting Helps in Efficient Management of IP Addresses
One of the main reasons for using subnetting is that it helps you to efficiently use the IP addresses. In a large network, while assigning a full block of IP addresses to a specific segment of the network might result in loss of a lot of unused addresses. Subnetting ensures that only the necessary number of IP addresses are allocated to each network segment.
Key Benefits of Subnetting:
- Improved Network Performance: By dividing a network into smaller subnets, you reduce network congestion and increase overall communication speeds.
- Enhanced Security: With subnetting, you can isolate sensitive sections of your network, such as the finance department, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Optimized IP Address Usage: Subnetting allows you to use IP addresses based on the actual size of the network, preventing wasted space.
The Concept of Subnet Masks and CIDR Notation
What is a Subnet Mask?
A subnet mask is used to separate the network portion from its host portion of an IP address. This helps in defining the range of IP addresses which belong to a particular network. A subnet mask is usually written in the form of four octets (e.g., 255.255.255.0), with the 255 values representing the network portion and the 0 values showing the host portion.
What is CIDR Notation?
CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing) notation is a modern way to represent the IP addresses and their subnet masks. Instead of relying on the traditional class system (A, B, C), CIDR uses a slash (/), which is followed by a number that indicates how many bits of the IP address are dedicated to the network portion.
For example:
- The 192.168.1.0/24 means that the first 24 bits are reserved for the network, which leaves the fourth octet for the host addresses. In this case, 254 usable IP addresses are available for devices.
The Process of Subnetting an IP Address
Subnetting includes the following steps:
- Convert the IP Address to Binary: Each IP address can be converted into its binary form for its better understanding of how the subnet mask are applied.
- Example: 192.168.5.0 will be represented in binary as:
- 11000000.10101000.00000101.00000000
- Apply the Subnet Mask: By using a subnet mask (e.g., /24), we define that the starting 24 bits of the IP address that are representing the network portion.
- Calculate the Usable Hosts: Once the network bits are determined, then the remaining bits are used for configuration of the hosts. For example, a /24 network has 256 total IP addresses, however, only 254 are usable (after excluding the network address and broadcast address).
Example of Subnetting: Understanding with a Practical Scenario
Let’s look at a real-world example to see how subnetting works.
Scenario: You are tasked with designing the network for a small company. The base IP address for the network is 192.168.5.0/24.
- Network address: 192.168.5.0
- Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0 (or /24)
- First usable host: 192.168.5.1 (usually the router IP)
- Last usable host: 192.168.5.254
- Broadcast address: 192.168.5.255
- Maximum number of hosts: 254
The IP range for usable hosts is from 192.168.5.1 to 192.168.5.254. This allows the devices in the network to communicate with each other without any conflicts.
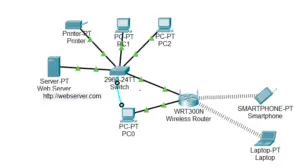
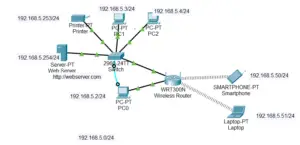
IP Address Allocation Table:
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Subnet Mask | Default Gateway |
| Wireless router | LAN | 192.168.5.1 | 255.255.255.0 | – |
| Web server | Fast Ethernet 0 | 192.168.5.254 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.5.1 |
| Printer | Fast Ethernet 0 | 192.168.5.253 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.5.1 |
| PC0 | Fast Ethernet 0 | 192.168.5.2 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.5.1 |
| PC1 | Fast Ethernet 0 | 192.168.5.3 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.5.1 |
| Laptop | Wireless 0 | Assigned by DHCP | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.5.1 |
This table shows the allotment of the IP addresses to various devices in the network, to ensure proper communication and efficient use of available IP addresses.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is subnetting in networking?
- Subnetting divides a large network into smaller, more efficient sub-networks to manage traffic, increase security, and optimize IP address usage.
- Why is subnetting important?
- Subnetting helps conserve IP address space, reduces network congestion, and enhances security by isolating different network segments.
- What is the difference between an IP address and a subnet mask?
- An IP address identifies a device on the network, while the subnet mask defines the size of the network portion and the host portion.
- What is CIDR notation?
- CIDR notation is a way of expressing IP addresses and subnet masks, using a slash followed by the number of bits in the network portion (e.g., 192.168.5.0/24).
- How do I calculate subnets and hosts in a network?
- Count the number of bits borrowed for subnetting to calculate subnets. For hosts, subtract 2 from the total number of addresses (for network and broadcast).
- What is the maximum number of hosts in a /24 subnet?
- A /24 subnet has 256 addresses, but 2 are reserved for the network and broadcast addresses, leaving 254 usable hosts.
By understanding subnetting and using CIDR notation, you can design an efficient, and secure networks. Whether you’re managing a small home network or a large enterprise system, subnetting is an essential skill for the network administrators and IT professionals to manage the networks. If you need more help, feel free to ask questions in the comments below!